Causes of urinary incontinence
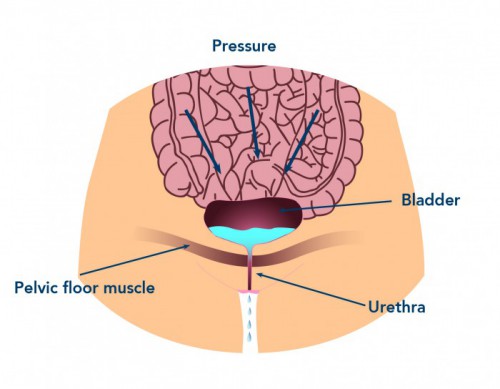
Women are particularly susceptible to stress incontinence due to the composition of the various structures in the pelvis and pelvic floor, and their interaction with each other. These factors are compounded by the effects of pregnancy and childbirth, as well as hormonal influences.
When the pelvic floor weakens and the tissue supporting the urethra becomes loose, the urethra may drop and widen. This results in an involuntary loss of urine whenever pressure increases in the abdomen (e.g. coughing, sneezing…). At the same time other prolapse problems, such as the uterus and vagina dropping down, or a bowel weakness with involuntary loss of gas or stool may occur.